Solar PV, or solar photovoltaics, harnesses solar radiation to create electricity. Because solar PV systems are affordable and have positive environmental effects, they are growing in popularity. Since solar energy is renewable, it may be utilised without diminishing the natural resources of the planet. Solar photovoltaic systems have a long lifespan and require little maintenance. Modern solar panels use sunlight to generate power; they don’t need direct sunlight to function, though they perform best on clear, sunny days when the sun is shining.
Solar photovoltaic (PV) technology uses thin silicon or other semiconducting material sheets to directly convert sunlight into power. The photovoltaic cells of the solar panel use sunlight absorption to generate electricity, which powers homes and businesses. Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems emit no emissions when in operation, which makes them a very appealing alternative to fossil fuel energy. Because it is affordable and has the potential to lower energy costs, solar photovoltaic (PV) technology is gaining popularity as a renewable energy source. As solar PV systems become more economical and effective, they will likely replace conventional energy sources.
Apart from their apparent advantages for the environment, solar cells also provide a great lot of versatility. They can be mounted on rooftops or other surfaces and utilised in both business and residential contexts. To establish a hybrid energy system, solar PV systems can also be linked with other energy sources like batteries and wind turbines. Solar panels can be installed almost anyplace with good sunshine, including large-scale solar farms, grazing pasture, and rooftops.
Solar panels also require little maintenance and can last up to 25 years with proper care.
They also allow households to reduce their energy bills and become more energy independent.
How does Solar PV Work?
Semiconductor cells are used in solar photovoltaic (PV) panels to convert solar energy into electricity. Sand is a natural source of silicon, a material that is used to make almost all semi-conductors. When light enters the cell, the semiconductor material absorbs some energy, which loosens the electrons—the negatively charged particles that are the building blocks of electricity.
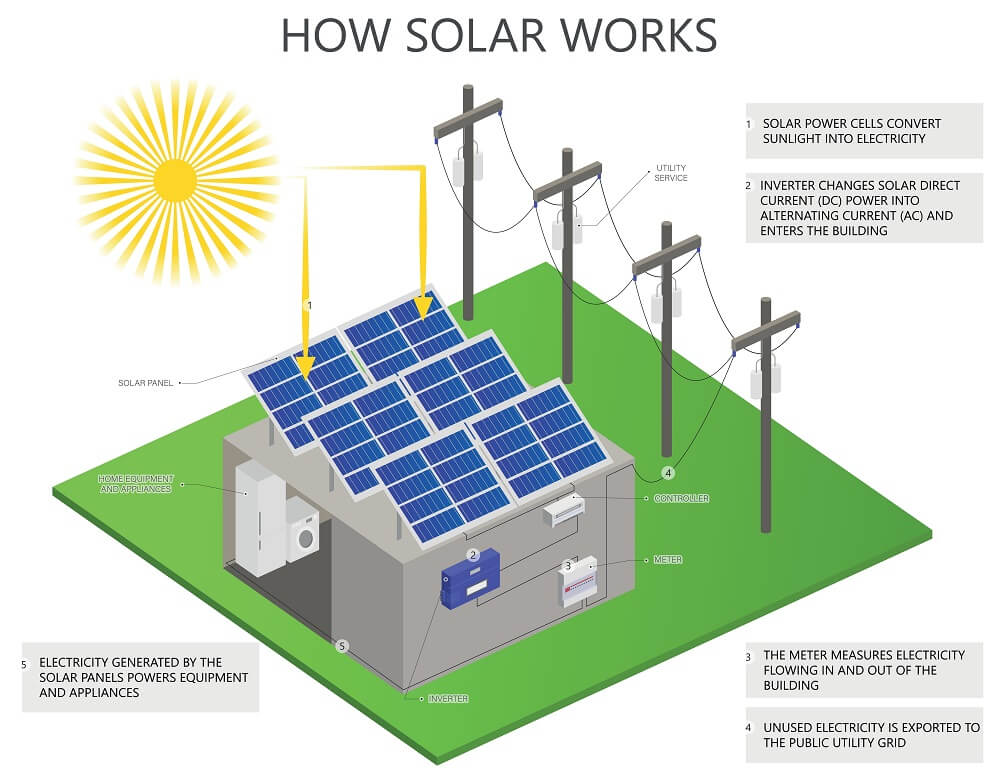
Two semiconductor material layers, with a positive charge and the other a negative charge, are frequently seen in photovoltaic cells. Electricity flows through a semi-conductor when light shines on it because this creates an electric field across the junction of these two layers. We can pull current from a PV cell externally by attaching metal contacts to the top and bottom of the cell.
Solar PV electric panels do not need direct sunlight to function, thus they can produce power even on gloomy days. Nevertheless, the more intense the sunshine, the more electricity the panels can produce. But because of the sun, days with a few clouds can produce more energy than those with a clear sky.
You will be charged for your energy usage as usual when the solar panels are not producing electricity because solar energy can only be used when it is being generated. Unless you also buy batteries to store power for use in the evenings and at night, you will be charged for your energy use.
Solar PV Inverters
An inverter is a component of your solar panel system that changes the direct current (DC) electricity that the panels capture into alternating current (AC). Your appliances are powered by AC current, which also connects your house to the national electricity grid. Depending on the nation, the voltage typically ranges from 120 to 240 volts. You could not safely use the energy you create from the sun to power your home without a solar inverter to transform sunlight energy into clean energy and electricity.
It is true that a solar panel system’s weakest component determines how efficient the system is, thus you should make sure the inverter you choose to go with your solar panel system is of the highest calibre. Often, inverters are forgotten about during design. Power for any photovoltaic system that runs on solar batteries will come from the inverters.
Some of their key characteristics are as follows:
- Alternating current can be created from direct current.
- Boosting output power to the greatest extent feasible.
- Interface with the National Grid.
- Offering input regarding power production.
- Preserving your solar PV system’s security.
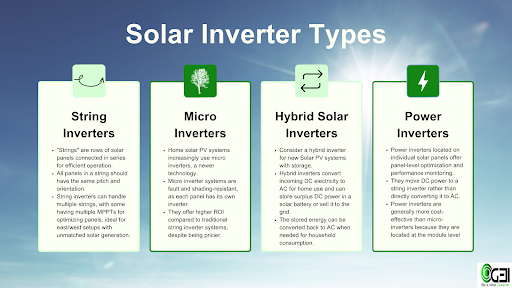
The Different Types Of Solar Inverters
There are four main types of solar inverters. Inverters can be broken down into string inverters, microinverters, hybrid inverters, and power optimisers. Below, we will explore the key characteristics of each kind of solar panel inverter. It couldn’t be easier to find the right solar inverter for your system.
Solar inverters are categorised into four primary categories. String inverters, microinverters, hybrid inverters, and power optimizers are the different types of inverters. We shall examine the salient features of each type of solar panel inverter below. Locating the ideal solar inverter for your system couldn’t be simpler.
String Inverters
‘Solar panel “strings” are collections or rows that are connected in series. For a string inverter to work properly, each panel in the string must be at the same pitch and orientation. A single inverter can handle multiple strings, and some string inverters include two or three MPPTs (Maximum Power Point Tracking features). It is possible to set up an individual MPPT with a separate solar panel string. In an east/west configuration, where the sun generation of the two strings of panels is unequal, it is perfect.
Micro Inverters
Micro inverters are a relatively new technology that are being used more and more in home solar PV systems. Unlike a string inverter with solar panels, an inverter system with a micro inverter is unaffected by defects or shadowing on individual panels. Any problems in a microinverter system are isolated because every solar panel has its own inverter. As a result, installing more solar panels is frequently thought to be best accomplished with microinverters. since it is no longer necessary to mix orientations or avoid shaded locations. Despite being generally more expensive, a micro inverter system offers a higher return on investment than a traditional string inverter system.
Hybrid Solar Inverters
A hybrid inverter is something you should take into consideration when establishing a new solar PV system with storage. We are aware that the DC electricity produced by solar panels needs to be converted into AC electricity by an inverter to power the gadgets in your house. On the other hand, DC electricity is stored in solar batteries. In addition to converting incoming DC power to AC, a hybrid solar inverter can transfer any excess DC power to be stored in a solar battery or sold to the grid. You can then convert the electricity to AC to use in your home when your stored energy is needed.
Power Inverters
Power inverters have many of the same advantages as micro-inverters and are also found on each individual panel. Performance monitoring and panel-level tuning are offered by power inverters, also known as DC power optimisers. The optimiser transfers DC power to a string inverter rather than converting it straight to AC like micro-inverters do. Probably positioned adjacent to your battery storage system is another battery storage system. As they are positioned at the module level, they are typically more affordable than micro-inverters.
Do solar panels increase home value?
It makes sense to future-proof our home investments in terms of both our current affordability and the value of our properties in the future, as housing costs and living expenses are expected to rise. Since solar PV panels come in a variety of sizes, installation is possible in any type of home.
Making energy-saving improvements is one of the greatest methods to raise the value of your house, and if your home goes from a G to an A rating, a high energy performance certificate (EPC) rating can result in a value rise of up to 14%.
Joining the 970,000+ UK homes who have already installed solar panels to lower their electricity bills is a fantastic option if you can afford the initial investment and continuing maintenance costs of solar panels, as well as the knowledge that your house is a potential candidate for solar panels. Inverters typically last 15 years, but solar panels often last 25.

